- Write a RESTful API with Ballerina
- Write a gRPC service with Ballerina
- Write a GraphQL API with Ballerina
- Work with data using queries in Ballerina
- Build a data service in Ballerina
- Build a Change Data Capture (CDC) service in Ballerina
- Work with Large Language Models (LLMs) using natural expressions
- Deploy Ballerina on Kubernetes
- Manage data persistence with bal persist
- Create your first connector with Ballerina
This guide helps you understand the basics of Ballerina constructs, which allow you to work with data services.
Set up the prerequisites
To complete this tutorial, you need:
- Ballerina 2201.0.0 (Swan Lake) or greater
- A text editor
Tip: Preferably, Visual Studio Code with the Ballerina extension installed.
- A command terminal
Understand the implementation
This tutorial describes how to connect to a MySQL database and perform queries against it using Ballerina via a basic use case of creating, maintaining, and interacting with a database of employees in an organization. It also elaborates on how you can create an HTTP RESTful API using Ballerina that can be used to perform basic CRUD operations on the database.
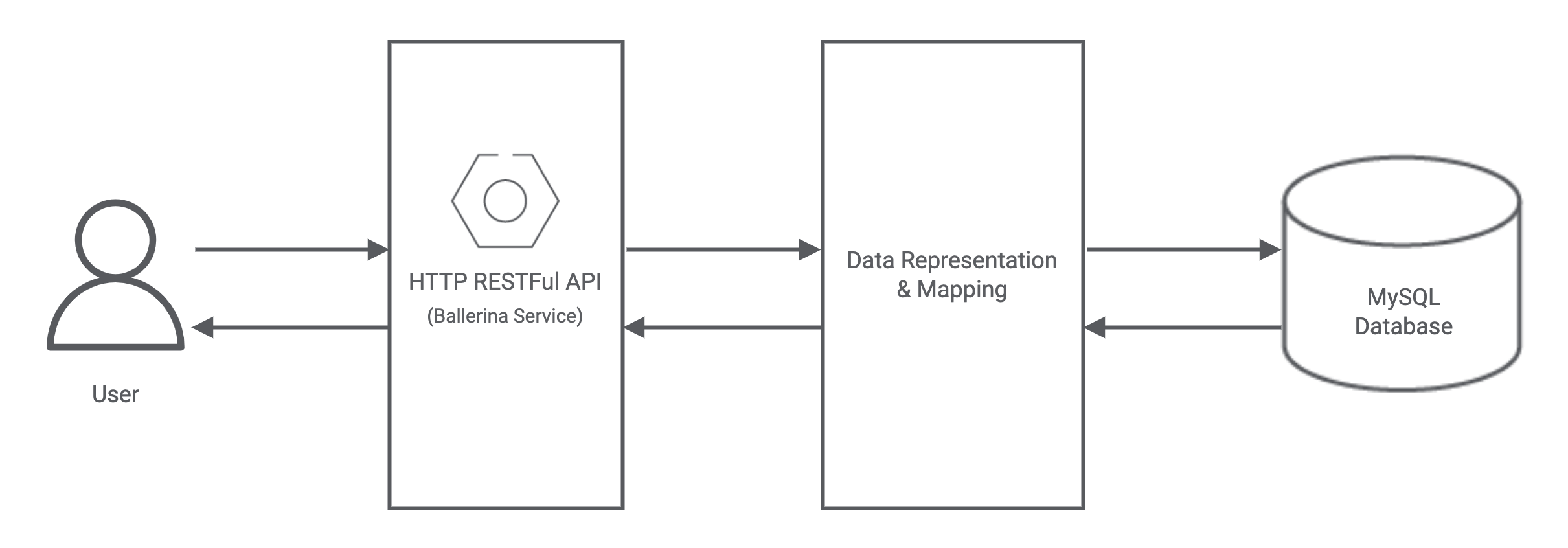
Info: The outlined methodology can be used to work with PostgreSQL, SQL Server, OracleDB, or any other relational database as well using the
PostgreSQL,MSSQL,OracleDB, andJDBCconnectors for Ballerina respectively.
Set up a MySQL server instance
Select one out of the methods below to set up a MySQL server.
Tip: Keep the connection and authentication details for connecting to the MySQL server including the hostname, port, username and password noted down.
- Install a MySQL server on your machine locally by downloading and installing MySQL for different platforms.
- Use a cross-platform web-server solution such as XAMPP or WampServer.
- Use Docker to create a MySQL server deployment.
- Use a cloud-based MySQL solution such as Google’s CloudSQL, Amazon’s RDS for MySQL, or Microsoft’s Azure database for MySQL.
Create a database and table
Connect to the MySQL server using the terminal (or any other preferred method), and execute the commands below to create a database and table.
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS Company; CREATE TABLE Company.Employees ( employee_id INTEGER AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, first_name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, last_name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, email VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, phone VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL , hire_date DATE NOT NULL, manager_id INTEGER REFERENCES Employees(employee_id), job_title VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL );
Create the service package
Ballerina uses packages to group code. You need to create a Ballerina package and write the business logic in it. In the terminal, execute the command below to create the Ballerina package for the implementation.
Info: For more information on Ballerina packages, see Organize Ballerina code.
$ bal new data_service
This creates a directory named data_service with the files below.
. ├── data_service │ ├── Ballerina.toml │ └── main.bal
Tip: Remove the automatically-created
main.balfile as you are not going to use it in this guide.
Create the service
Create a record to represent an employee
In Ballerina, records are a data type that maps keys to values. Define a closed record to represent a single row in the Employees table in the main.bal file.
Info: This record type is the basis for interacting with the database.
import ballerina/time; public type Employee record {| int employee_id?; string first_name; string last_name; string email; string phone; time:Date hire_date; int? manager_id; string job_title; |};
Add the MySQL driver
The MySQL driver JAR is necessary to connect to and interact with a MySQL server. Select one out of the methods below to add it.
-
Import the
ballerinax/mysql.driverpackage in yourmain.balfile. This package bundles the latest MySQL driver so that the MySQL connector can be used in Ballerina packages easily.import ballerinax/mysql.driver as _; -
Update the
Ballerina.tomlfile with the Maven dependency params for the MySQL driver.[[platform.java11.dependency]] groupId = "mysql" artifactId = "mysql-connector-java" version = "8.0.26" -
Download the driver JAR manually and update the path in the
Ballerina.tomlfile[[platform.java11.dependency]] path = "/path/to/mysql/driver.jar”
Define MySQL configurations
In the package directory, create a new file named Config.toml and specify the configurations below to connect to the MySQL database.
USER="root" PASSWORD="rootPassword" HOST="localhost" PORT=3306 DATABASE="Company"
To redefine the above variables and access them from within your Ballerina program, add the code below in the main.bal file.
configurable string USER = ?; configurable string PASSWORD = ?; configurable string HOST = ?; configurable int PORT = ?; configurable string DATABASE = ?;
Note: For more information on defining configurable variables in Ballerina, see Provide values to configurable variables.
Connect to the database
You can connect to the MySQL database by creating a client.
Import the required packages
To import the mysql
and sql packages for creating the client, add the code below in the main.bal file.
import ballerinax/mysql; import ballerina/sql;
Create the MySQL client
To use the mysql:Client to the database, add the code below in the main.bal file.
final mysql:Client dbClient = check new( host=HOST, user=USER, password=PASSWORD, port=PORT, database="Company" );
Run the MySQL client
Execute the command below to run the client.
$ bal run
If the program runs without throwing an error, that indicates that the connection has been established successfully. This client can be defined globally and be used across all parts of the program.
Info: The MySQL package provides additional connection options and the ability to configure connection pool properties when connecting to the database which, are not covered in this tutorial. To learn more about this, see
mysql:Client.
Execute the queries
The mysql:Client provides two primary remote methods for performing queries.
-
query()- Executes an SQL query and returns the results (rows) from the query. ThequeryRow()method is a variation of this method, which returns at most a single row from the result. -
execute()- Executes an SQL query and returns only the metadata of the execution.
To use the query(), queryRow(), and execute() methods, which can perform basic CRUD operations against the MySQL database, add the code below to the main.bal file.
isolated function addEmployee(Employee emp) returns int|error { sql:ExecutionResult result = check dbClient->execute(` INSERT INTO Employees (employee_id, first_name, last_name, email, phone, hire_date, manager_id, job_title) VALUES (${emp.employee_id}, ${emp.first_name}, ${emp.last_name}, ${emp.email}, ${emp.phone}, ${emp.hire_date}, ${emp.manager_id}, ${emp.job_title}) `); int|string? lastInsertId = result.lastInsertId; if lastInsertId is int { return lastInsertId; } else { return error("Unable to obtain last insert ID"); } } isolated function getEmployee(int id) returns Employee|error { Employee employee = check dbClient->queryRow( `SELECT * FROM Employees WHERE employee_id = ${id}` ); return employee; } isolated function getAllEmployees() returns Employee[]|error { Employee[] employees = []; stream<Employee, error?> resultStream = dbClient->query( `SELECT * FROM Employees` ); check from Employee employee in resultStream do { employees.push(employee); }; check resultStream.close(); return employees; } isolated function updateEmployee(Employee emp) returns int|error { sql:ExecutionResult result = check dbClient->execute(` UPDATE Employees SET first_name = ${emp.first_name}, last_name = ${emp.last_name}, email = ${emp.email}, phone = ${emp.phone}, hire_date = ${emp.hire_date}, manager_id = ${emp.manager_id}, job_title = ${emp.job_title} WHERE employee_id = ${emp.employee_id} `); int|string? lastInsertId = result.lastInsertId; if lastInsertId is int { return lastInsertId; } else { return error("Unable to obtain last insert ID"); } } isolated function removeEmployee(int id) returns int|error { sql:ExecutionResult result = check dbClient->execute(` DELETE FROM Employees WHERE employee_id = ${id} `); int? affectedRowCount = result.affectedRowCount; if affectedRowCount is int { return affectedRowCount; } else { return error("Unable to obtain the affected row count"); } }
The main.bal file complete code
import ballerina/time; import ballerinax/mysql; import ballerinax/mysql.driver as _; // This bundles the driver to the project so that you don't need to bundle it via the `Ballerina.toml` file. import ballerina/sql; public type Employee record {| int employee_id?; string first_name; string last_name; string email; string phone; time:Date hire_date; int? manager_id; string job_title; |}; configurable string USER = ?; configurable string PASSWORD = ?; configurable string HOST = ?; configurable int PORT = ?; configurable string DATABASE = ?; final mysql:Client dbClient = check new( host=HOST, user=USER, password=PASSWORD, port=PORT, database="Company" ); isolated function addEmployee(Employee emp) returns int|error { sql:ExecutionResult result = check dbClient->execute(` INSERT INTO Employees (employee_id, first_name, last_name, email, phone, hire_date, manager_id, job_title) VALUES (${emp.employee_id}, ${emp.first_name}, ${emp.last_name}, ${emp.email}, ${emp.phone}, ${emp.hire_date}, ${emp.manager_id}, ${emp.job_title}) `); int|string? lastInsertId = result.lastInsertId; if lastInsertId is int { return lastInsertId; } else { return error("Unable to obtain last insert ID"); } } isolated function getEmployee(int id) returns Employee|error { Employee employee = check dbClient->queryRow( `SELECT * FROM Employees WHERE employee_id = ${id}` ); return employee; } isolated function getAllEmployees() returns Employee[]|error { Employee[] employees = []; stream<Employee, error?> resultStream = dbClient->query( `SELECT * FROM Employees` ); check from Employee employee in resultStream do { employees.push(employee); }; check resultStream.close(); return employees; } isolated function updateEmployee(Employee emp) returns int|error { sql:ExecutionResult result = check dbClient->execute(` UPDATE Employees SET first_name = ${emp.first_name}, last_name = ${emp.last_name}, email = ${emp.email}, phone = ${emp.phone}, hire_date = ${emp.hire_date}, manager_id = ${emp.manager_id}, job_title = ${emp.job_title} WHERE employee_id = ${emp.employee_id} `); int|string? lastInsertId = result.lastInsertId; if lastInsertId is int { return lastInsertId; } else { return error("Unable to obtain last insert ID"); } } isolated function removeEmployee(int id) returns int|error { sql:ExecutionResult result = check dbClient->execute(` DELETE FROM Employees WHERE employee_id = ${id} `); int? affectedRowCount = result.affectedRowCount; if affectedRowCount is int { return affectedRowCount; } else { return error("Unable to obtain the affected row count"); } }
Expose the database via an HTTP RESTful API
After you have defined the methods necessary to manipulate the database, expose these selectively via an HTTP RESTful API.
Import the required packages
For this, create a file named service.bal inside the Ballerina package directory (ata_service), and add the code below to import the Ballerina HTTP module.
import ballerina/http;
Create a service
To create the service, add the code below to the service.bal file.
service /employees on new http:Listener(8080) { }
Create the resource methods
Within this service, you can define resource methods to provide access to the database. The code snippet below
demonstrates a resource method that can be used to create a new employee via a POST request.
service /employees on new http:Listener(8080) { isolated resource function post .(@http:Payload Employee emp) returns int|error? { return addEmployee(emp); } isolated resource function get [int id]() returns Employee|error? { return getEmployee(id); } isolated resource function get .() returns Employee[]|error? { return getAllEmployees(); } isolated resource function put .(@http:Payload Employee emp) returns int|error? { return updateEmployee(emp); } isolated resource function delete [int id]() returns int|error? { return removeEmployee(id); } }
The service.bal file complete code
The complete code in the service.bal will be as follows.
import ballerina/http; service /employees on new http:Listener(8080) { isolated resource function post .(@http:Payload Employee emp) returns int|error? { return addEmployee(emp); } isolated resource function get [int id]() returns Employee|error? { return getEmployee(id); } isolated resource function get .() returns Employee[]|error? { return getAllEmployees(); } isolated resource function put .(@http:Payload Employee emp) returns int|error? { return updateEmployee(emp); } isolated resource function delete [int id]() returns int|error? { return removeEmployee(id); } }
Run the service
Execute the command below to run the service.
$ bal run
You view the output below.
Compiling source foo/data_service:0.1.0 Running executable
Info: This creates an
/employeesendpoint on port8080, which can be accessed via a browser by visitinghttp://locahost:8080/employees.
Try the service
Invoke the defined resource method by sending the POST request below to http://localhost:8080/employees with the required data as a JSON payload.
$ curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/employees/ -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d "{ \"employee_id\": 6, \"first_name\": \"test\", \"last_name\": \"test\", \"email\": \"test@test.com\", \"phone\": \"882 771 110\", \"hire_date\": { \"year\": 2021, \"month\": 12, \"day\": 16 }, \"manager_id\": 1, \"job_title\": \"Sales Manager\" }"
You view a row added to the Employees table as shown below.

Learn more
To learn more about MySQL and HTTP support in Ballerina, see the following: