- Write a RESTful API with Ballerina
- Write a gRPC service with Ballerina
- Write a GraphQL API with Ballerina
- Work with data using queries in Ballerina
- Build a data service in Ballerina
- Build a Change Data Capture (CDC) service in Ballerina
- Work with Large Language Models (LLMs) using natural expressions
- Deploy Ballerina on Kubernetes
- Manage data persistence with bal persist
- Create your first connector with Ballerina
Ballerina provides metrics compatible with Prometheus, which is widely used worldwide to monitor open-source systems.
The sample shop service will be used in this guide. Follow the steps given below to observe Ballerina metrics in Prometheus.
Step 1 - Set up Prometheus
Prometheus is used as the monitoring system, which pulls out the metrics collected from the Ballerina /metrics service. This section focuses on the quick installation of Prometheus with Docker and the configuration required to collect metrics from the Ballerina service with the default configurations. Follow the steps below to configure Prometheus.
Tip: There are many other ways to install Prometheus and you can find possible options from the installation guide. The easiest option is to use precompiled binaries listed in Downloads.
-
Create a
prometheus.ymlfile in a directory. -
Add the following content to the
prometheus.ymlfile.global: scrape_interval: 15s evaluation_interval: 15s scrape_configs: - job_name: 'prometheus' static_configs: - targets: ['a.b.c.d:9797']Here, the
'a.b.c.d:9797'targets should contain the host and port of the/metricsservice that is exposed from Ballerina for metrics collection. Add the IP of the host in which the Ballerina service is running asa.b.c.dand its port (default9797). If you need more information, go to the Prometheus documentation. If your Ballerina service is running on localhost and Prometheus in a Docker container, add the target ashost.docker.internal:9797to access the localhost from Docker. -
Start the Prometheus server in a Docker container with the command below.
$ docker run -p 9090:9090 -v <path_to_prometheus.yml>:/etc/prometheus/ prom/prometheus
Step 2 - Import Ballerina Prometheus extension
To include the Prometheus extension into the executable, the ballerinax/prometheus module needs to be imported into your Ballerina project main.bal file.
import ballerinax/prometheus as _;
To support Prometheus as the metrics reporter, an HTTP endpoint starts with the context of /metrics in the default port 9797 when starting the Ballerina service.
Step 3 - Configure Ballerina runtime configurations
You can set up Prometheus for your Ballerina project using configurations similar to the following in your Config.toml file.
[ballerina.observe] metricsEnabled=true metricsReporter="prometheus" [ballerinax.prometheus] port=9797 host="0.0.0.0"
| Configuration key | Description | Default value | Possible values |
|---|---|---|---|
ballerinax.prometheus.port | The value of the port to which the '/metrics' service will bind. This service will be used by Prometheus to scrape the information of the Ballerina service. | 9797 | Any suitable value for port 0 - 0 - 65535. However, within that range, ports 0 - 1023 are generally reserved for specific purposes. Therefore, it is advisable to select a port outside that range. |
ballerinax.prometheus.host | The name of the host to which the '/metrics' service will bind. This service will be used by Prometheus to scrape the information of the Ballerina service. | 0.0.0.0 | IP or Hostname or 0.0.0.0 of the node in which the Ballerina service is running. |
Step 4 - Run the Ballerina service
When Ballerina observability is enabled, the Ballerina runtime exposes internal metrics via an HTTP endpoint (/metrics) for metrics monitoring, and the metrics will be published to Prometheus. Prometheus should be configured to scrape metrics from the metrics HTTP endpoint in Ballerina.
Run the following command to start the Ballerina service.
$ bal run Compiling source Running executable ballerina: started Prometheus HTTP listener 0.0.0.0:9797
Step 5 - Send requests
Send requests to http://localhost:8090/shop/products.
Example cURL commands:
$ curl -X GET http://localhost:8090/shop/products
$ curl -X POST http://localhost:8090/shop/product \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "id": 4, "name": "Laptop Charger", "price": 50.00 }'
$ curl -X POST http://localhost:8090/shop/order \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "productId": 1, "quantity": 1 }'
$ curl -X GET http://localhost:8090/shop/order/0
Step 6 - View metrics on the Prometheus server
Go to http://localhost:19090/ and check whether you can see the Prometheus graph. Ballerina metrics should appear in the Prometheus graph's metrics list when the Ballerina service is started.
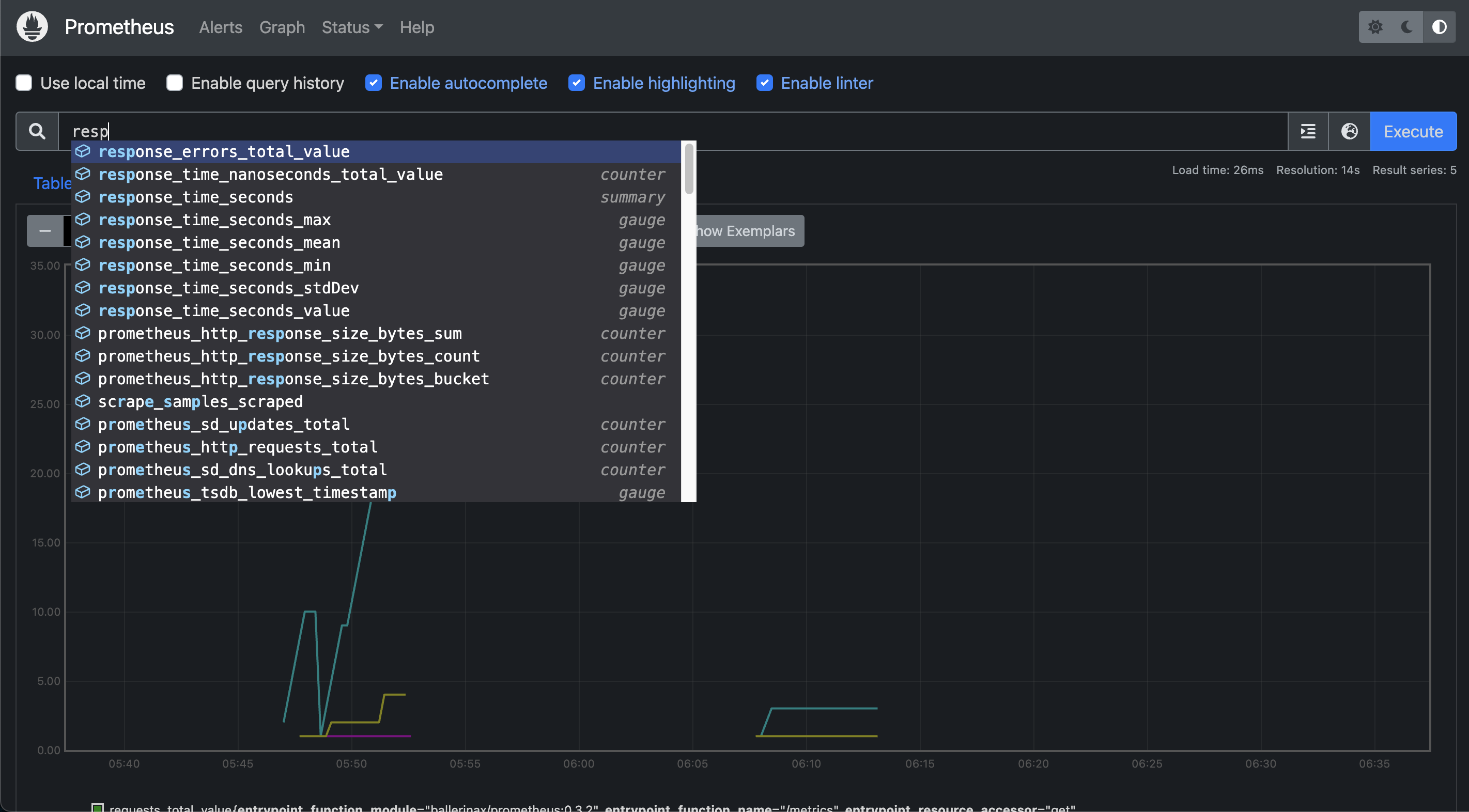
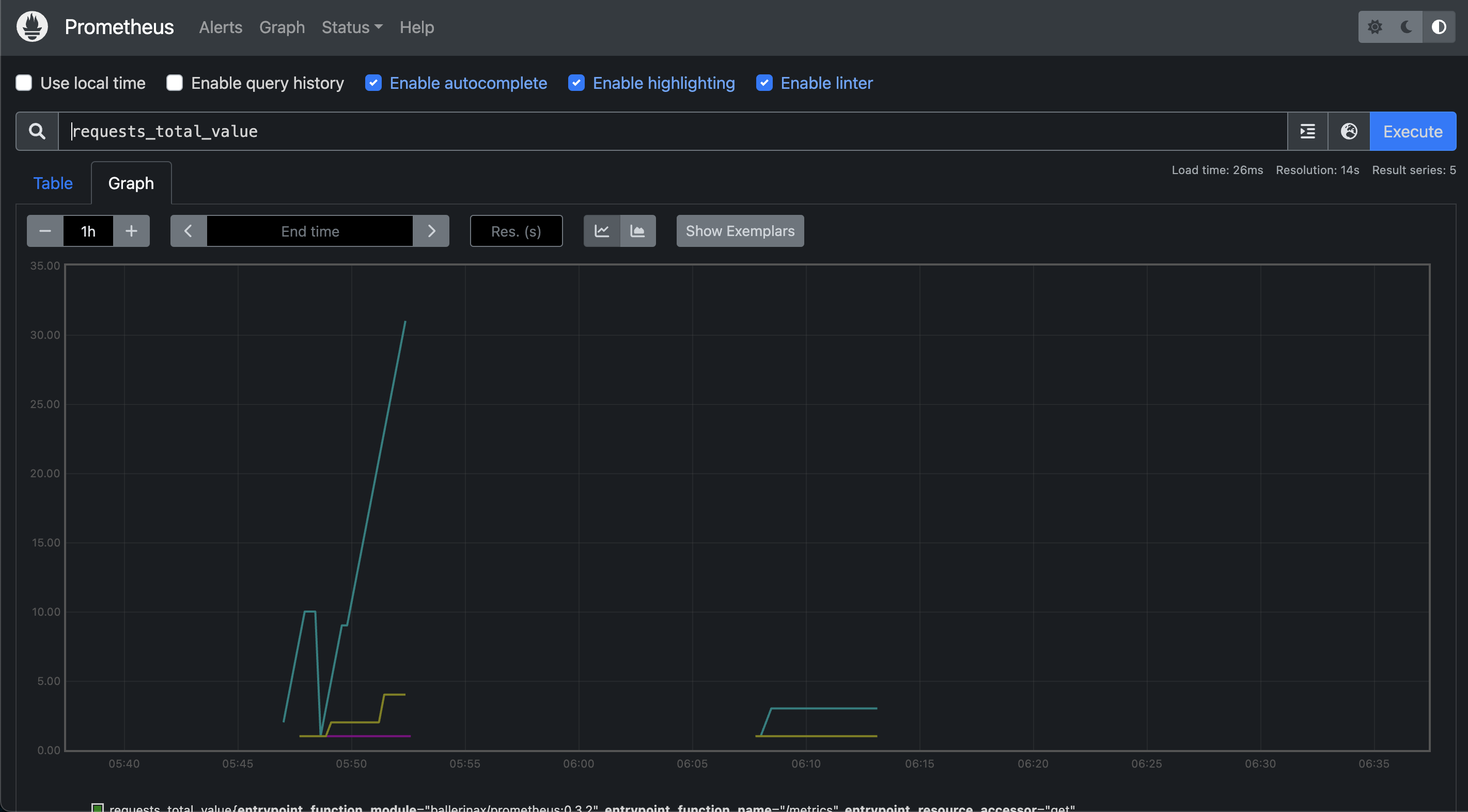
You can also use the following command to get the metrics.
$ curl http://localhost:9797/metrics
Set up Grafana
Grafana can be used to visualize Ballerina metrics provided for Prometheus. First, users need to set up the Ballerina project to observe metrics in Prometheus and follow the steps mentioned above.
Let’s use Grafana to visualize metrics in a dashboard. For this, we need to install Grafana and configure Prometheus as a data source. Follow the steps below to configure Grafana.
-
Start Grafana as a Docker container with the command below.
$ docker run -d --name=grafana -p 3000:3000 grafana/grafanaFor more information, go to Grafana in Docker Hub.
-
Go to http://localhost:3000/ to access the Grafana dashboard running on Docker.
-
Login to the dashboard with the default user, username:
adminand password:admin -
Add Prometheus as a data source with the
Browseraccess configuration as provided below.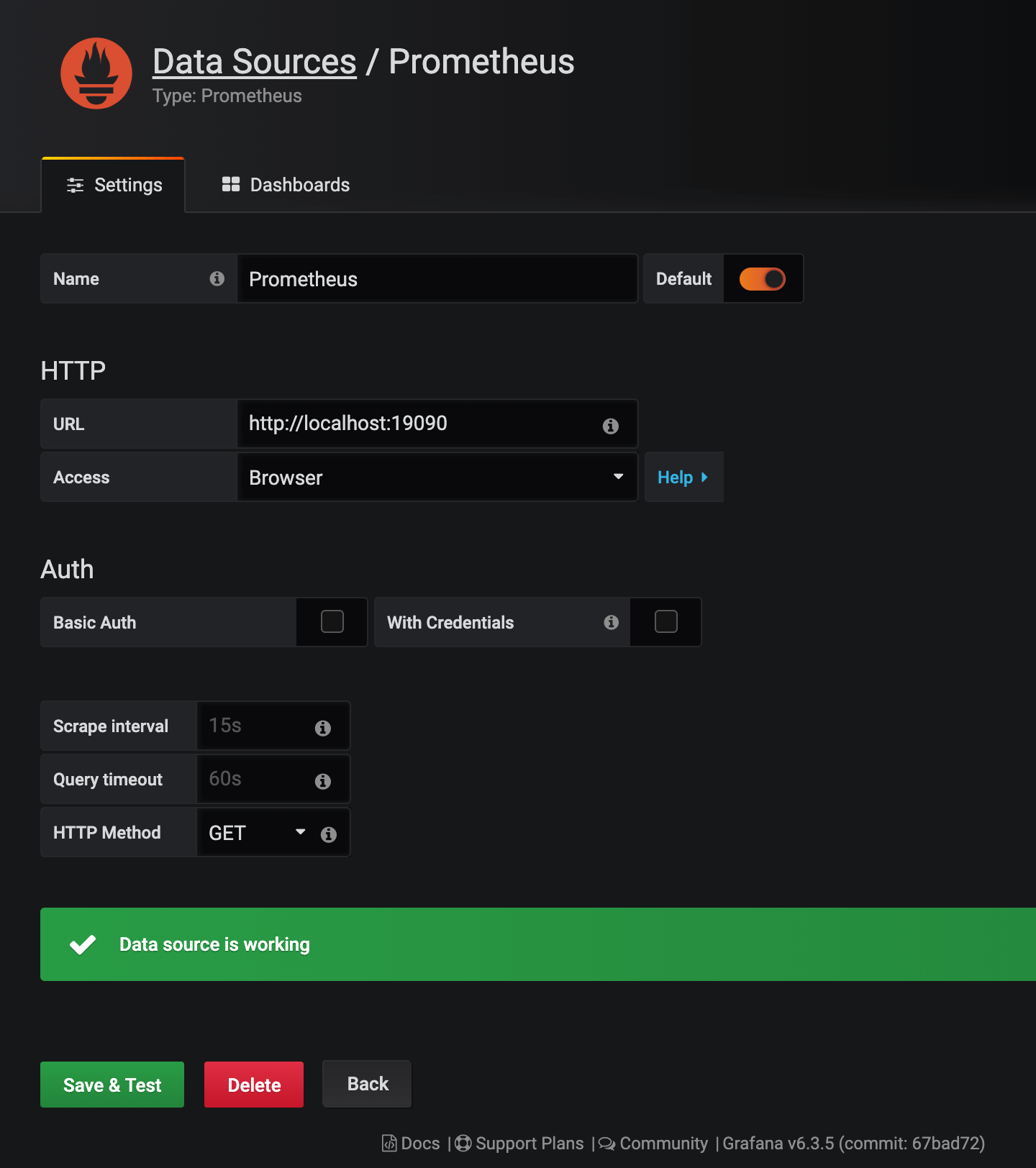
-
Import the Grafana dashboard designed to visualize Ballerina metrics from https://grafana.com/dashboards/5841 as shown below.
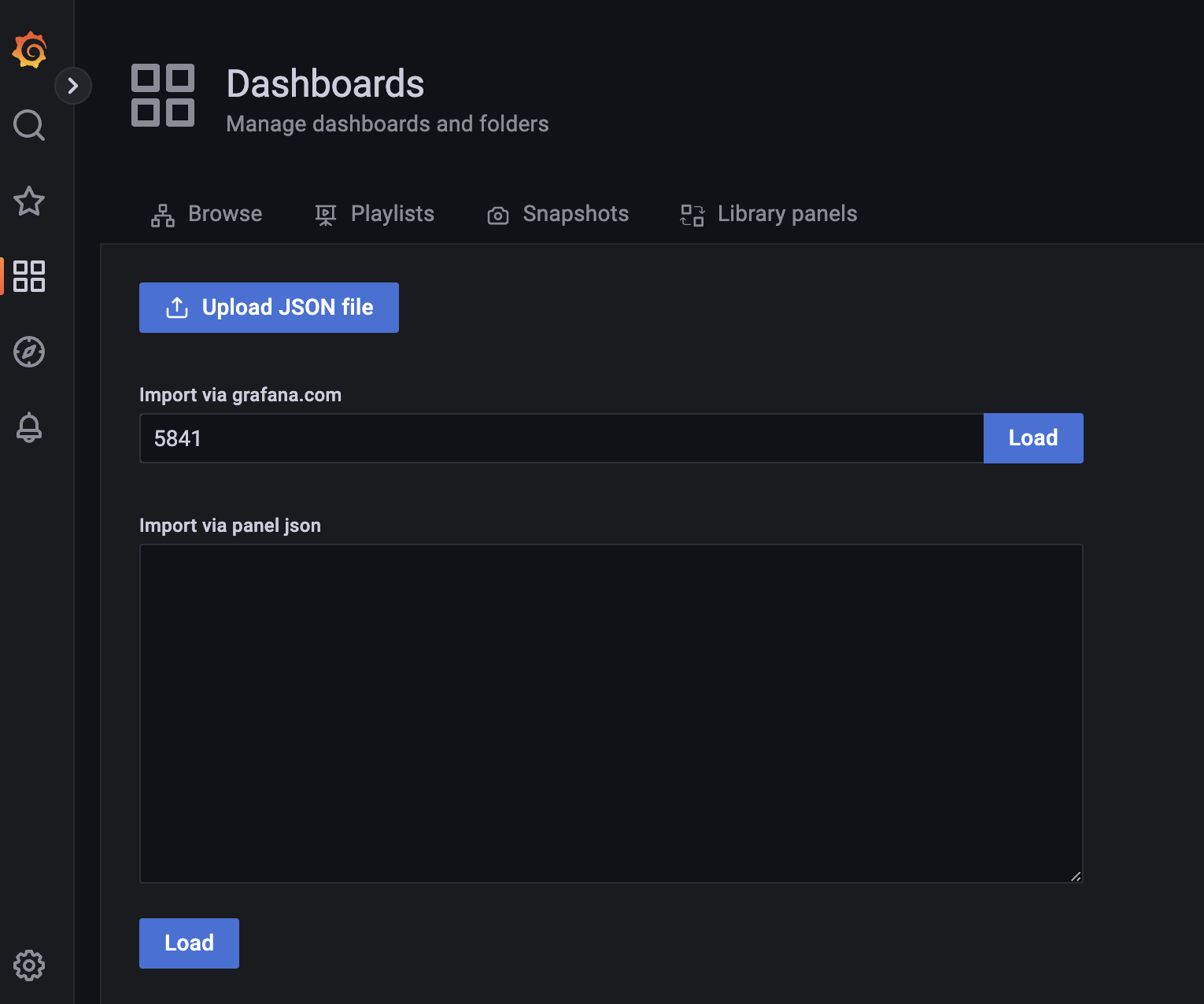
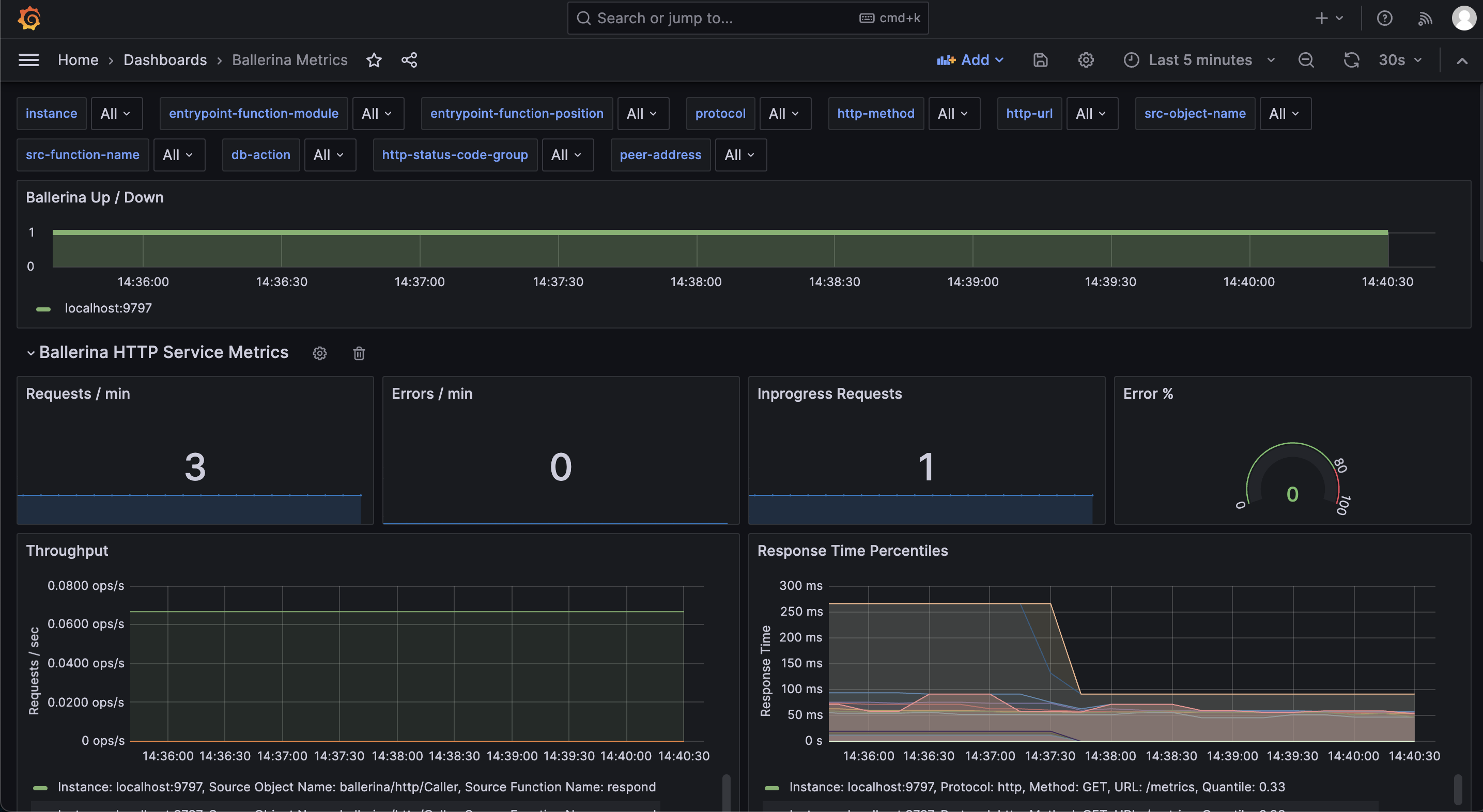
This dashboard consists of service and client invocation level metrics in near real-time view.
The Ballerina HTTP service metrics dashboard panel will be as shown below.