- Write a RESTful API with Ballerina
- Write a gRPC service with Ballerina
- Write a GraphQL API with Ballerina
- Work with data using queries in Ballerina
- Build a data service in Ballerina
- Build a Change Data Capture (CDC) service in Ballerina
- Work with Large Language Models (LLMs) using natural expressions
- Deploy Ballerina on Kubernetes
- Manage data persistence with bal persist
- Create your first connector with Ballerina
Users can configure Ballerina to support distributed tracing with Zipkin, which is one of the open-source and distributed tracing platforms that helps troubleshoot latency problems in service architectures. Ballerina provides tracing data in OpenTelemetry format.
The sample shop service will be used in this guide. Follow the steps given below to observe Ballerina tracing in Zipkin.
Step 1 - Set up Zipkin
You can configure Ballerina to support distributed tracing with Zipkin. This section focuses on configuring Zipkin with Docker as a quick installation.
Tip: There are many possible ways to deploy Zipkin. For more information, see Zipkin Quickstart.
Install Zipkin via Docker and start the Docker container by executing the command below.
$ docker run -d -p 9411:9411 openzipkin/zipkin
Step 2 - Import Ballerina Zipkin extension
To include the Zipkin extension into the executable, the ballerinax/zipkin module needs to be imported into your Ballerina project main.bal file.
import ballerinax/zipkin as _;
Zipkin extension has a Zipkin Span Exporter which will push tracing data as batches to the Zipkin server endpoint (default - http://localhost:9411) in Zipkin format.
Step 3 - Configure Ballerina runtime configurations
Tracing can be enabled in your Ballerina project using configurations similar to the following in your Config.toml file.
[ballerina.observe] tracingEnabled=true tracingProvider="zipkin" [ballerinax.zipkin] agentHostname="localhost" agentPort=9411 samplerType="const" samplerParam=1.0 reporterFlushInterval=1000 reporterBufferSize=10000
The table below provides the descriptions of each configuration option and possible values that can be assigned.
| Configuration key | Description | Default value | Possible values |
|---|---|---|---|
| ballerinax.zipkin. agentHostname | Hostname of the Zipkin agent | localhost | IP or hostname of the Zipkin agent. If it is running on the same node as Ballerina, it can be localhost. |
| ballerinax.zipkin. agentPort | Port of the Zipkin agent | 4317 | The port on which the Zipkin agent is listening. |
| ballerinax.zipkin. samplerType | Type of the sampling methods used in the Zipkin tracer. | const | const, probabilistic, or ratelimiting. |
| ballerinax.zipkin. samplerParam | It is a floating value. Based on the sampler type, the effect of the sampler param varies | 1.0 | For const 0 (no sampling) or 1 (sample all spans), for probabilistic 0.0 to 1.0, for ratelimiting any positive integer (rate per second). |
| ballerinax.zipkin. reporterFlushInterval | The Zipkin client will be sending the spans to the agent at this interval. | 2000 | Any positive integer value. |
| ballerinax.zipkin. reporterBufferSize | Queue size of the Zipkin client. | 2000 | Any positive integer value. |
Step 4 - Run the Ballerina service
When Ballerina observability is enabled, the Ballerina runtime collects tracing data and traces will be published to Zipkin.
Run the following command to start the Ballerina service.
$ bal run Compiling source Running executable ballerina: started publishing traces to Zipkin on http://localhost:9411
Step 5 - Send requests
Send requests to http://localhost:8090/shop/products.
Example cURL commands:
$ curl -X GET http://localhost:8090/shop/products
$ curl -X POST http://localhost:8090/shop/product \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "id": 4, "name": "Laptop Charger", "price": 50.00 }'
$ curl -X POST http://localhost:8090/shop/order \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "productId": 1, "quantity": 1 }'
$ curl -X GET http://localhost:8090/shop/order/0
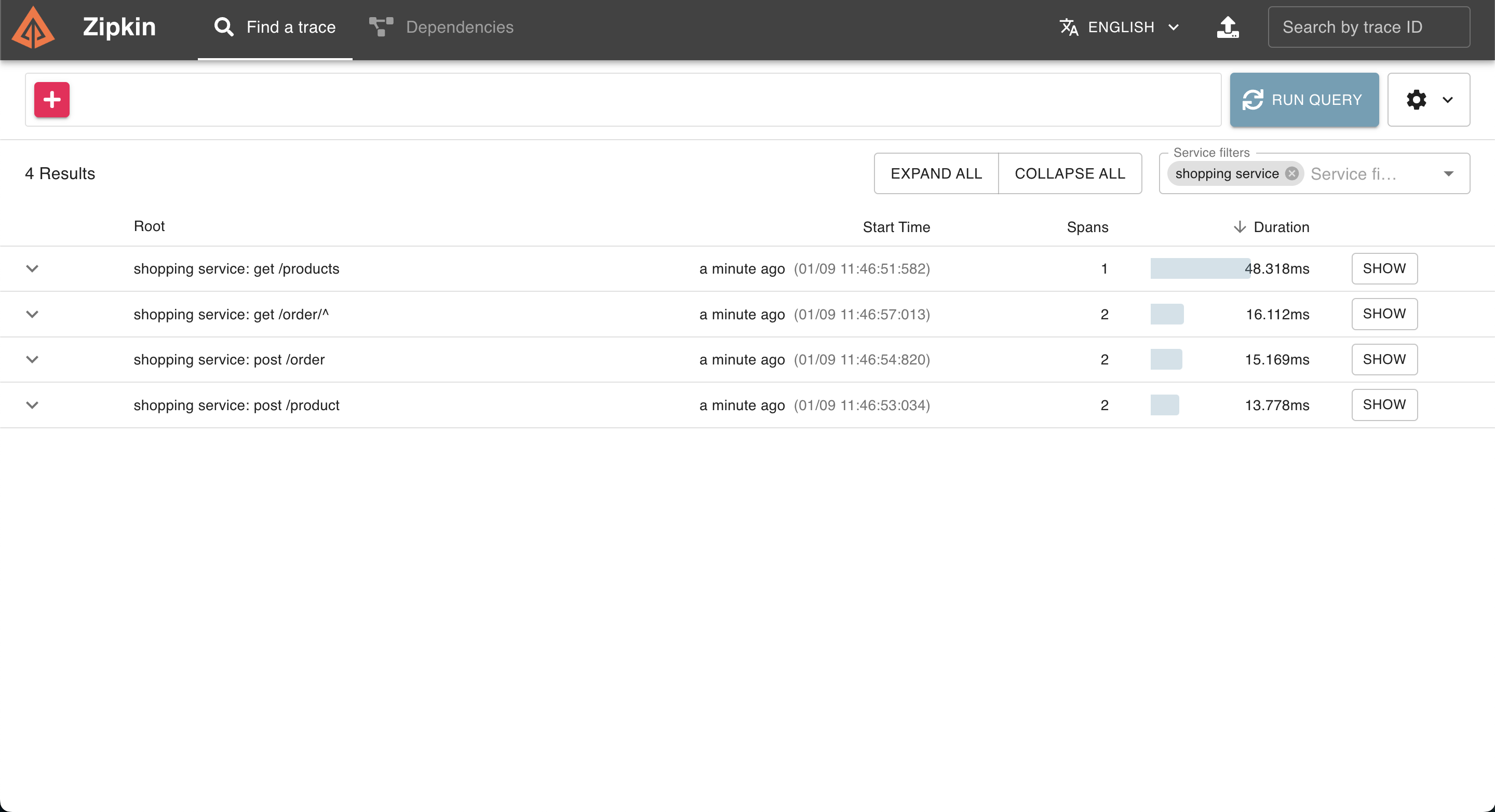
Step 6 - View distributed tracing on the Zipkin server
Go to http://localhost:9411 and load the web UI of Zipkin to make sure it is functioning properly. You can select the service for which you need tracing information find traces.
The image below is the sample tracing information you can see in Zipkin.