- Write a RESTful API with Ballerina
- Write a gRPC service with Ballerina
- Write a GraphQL API with Ballerina
- Work with data using queries in Ballerina
- Build a data service in Ballerina
- Build a Change Data Capture (CDC) service in Ballerina
- Work with Large Language Models (LLMs) using natural expressions
- Deploy Ballerina on Kubernetes
- Manage data persistence with bal persist
- Create your first connector with Ballerina
The bal persist feature allows you to store data in different data stores and retrieve them when needed. A data store can be a database or an in-memory cache. The bal persist feature currently supports in-memory tables, MySQL, MSSQL, PostgreSQL databases, Google Sheets, and Redis as data stores. As you can use the same syntax to access data in all these data stores, you do not need to learn different syntaxes to access data in different data stores.
This feature has three main components: the data model, CLI tool, and type-safe client API.
- Data model: The data model definition is used to define the data model.
- CLI tool: The CLI tool is used to generate the client API for the data model.
- Client API: The type-safe client API is used to access the data in the data store.
The following diagram illustrates how the bal persist feature works.
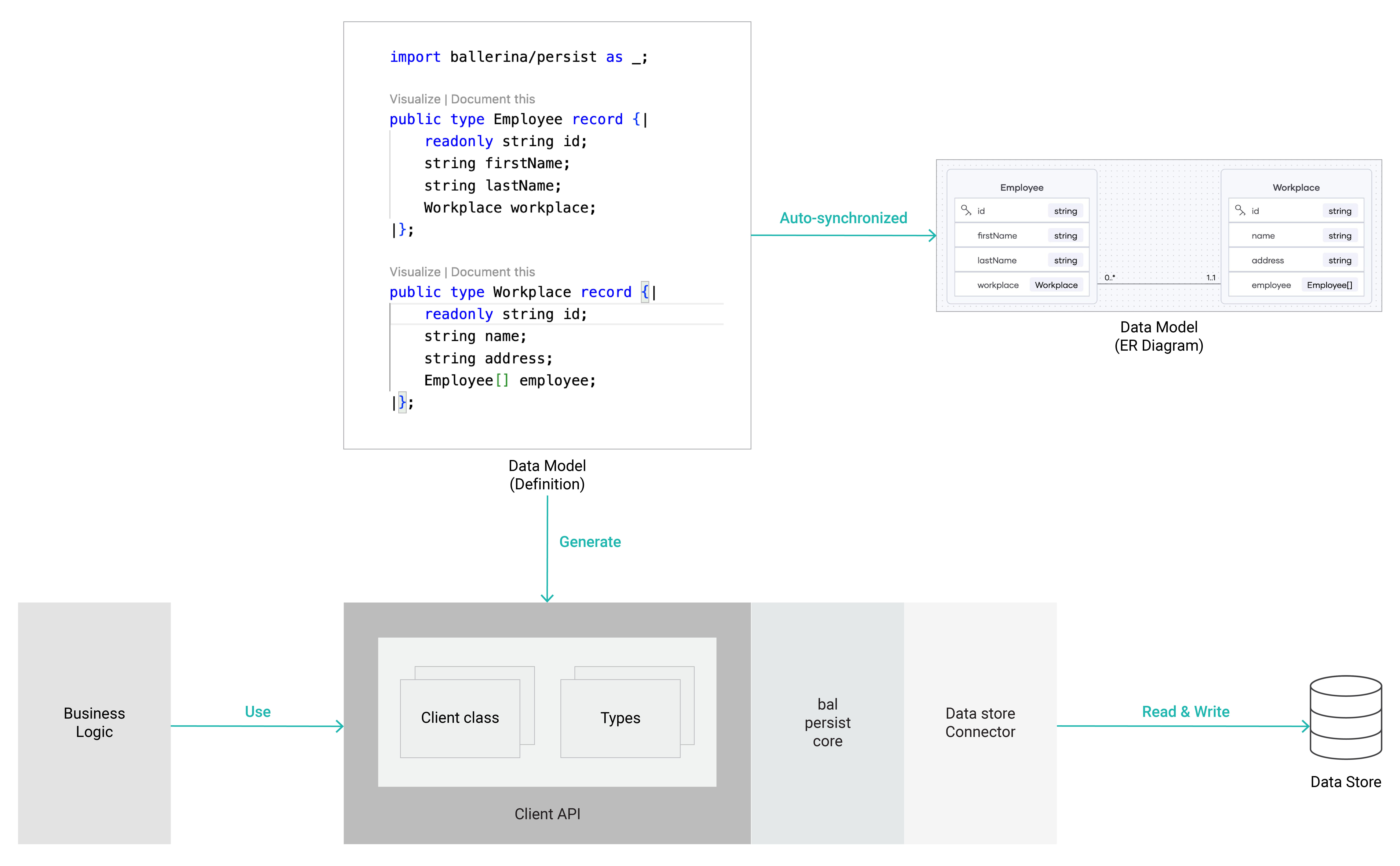
The data model definition shown in the above diagram is the source of truth for the data model of your application. The data model definition is used only to generate the client API, which contains the Ballerina client class and types. It cannot be used directly in your applications.
The Ballerina VS Code extension facilitates the validation, development (via code actions), and visualization (in an Entity Relationship diagram) of the data model definition when creating it.
The created data model definition will be used to generate the client API via the bal persist CLI tool as a Ballerina source file. You can import this generated client API into your Ballerina source files and use it in your business logic to access the data in the data store.
The following sections describe the data model, CLI tool, and client API in detail.
Data Model
The data model is defined in a Ballerina source file inside the persist directory in the project root directory. The data model is defined using the Ballerina record type. The following example shows how to define a data model for a table named Employee with the fields id, name, age, and salary.
type Employee record { readonly int id; string name; int age; float salary; }
The readonly keyword is used to define a field as a primary key. You need to have at least one primary key field in the Entity record. The primary key field is used to uniquely identify a record in the table. The primary key field is used to generate the get, update, and delete operations in the client API. You can define multiple primary key fields in the Entity record.
Learn about how to define relationships between entity records and more about data modeling in the Data Model section.
Note: The Ballerina VS Code plugin provides validation and code actions for the persist model. Therefore, you can easily create the Persist Model using the Ballerina VS Code plugin.
CLI tool
The bal persist CLI is used to generate the client API for the data model. With the integration of bal persist code generation into the bal build command, project building now automatically triggers the generation of Client APIs. Additionally, based on the data store, additional configurable files and setup scripts are also generated. For example, if you are using a relational database as the data store, the persist_db_config.bal file, and the script.sql script are generated. The persist_db_config.bal file is used to configure the relational database connection. The script.sql file is used to create the tables in the relational database. The client API is generated in the generated directory in the project root directory.
The bal persist has two built-in CLI commands: persist init and persist add to initialize bal persist in the Ballerina project. The persist init command solely establishes the persist directory and creates a data model file. Conversely, the persist add command not only creates the model file but also configures tools to integrate with bal build. If integration with bal build for code generation isn't desired, the persist generate command provides a one-time generation option.
The bal persist CLI tool also provides persist pull command, which facilitates introspection of an existing database to generate the data model. Currently, introspection is supported for MySQL, MSSQL, and PostgreSQL databases.
Furthermore, there is a experimental command: persist migrate. The persist migrate generates SQL scripts to alter the table structure in the database when modifications are made to the data model.
Learn more about bal persist CLI in the CLI tool section.
Type-safe client API
The client API is used to access the data in the data store. The client API is generated using the CLI tool, and it is located in the generated directory in the project root directory. The client API consists of a Ballerina client object with a resource for each entity record modeled in the Ballerina project. For each client resource, there are resource methods to perform CRUD operations on the data store.
For example, if you have an Employee entity record in the Ballerina project, you can perform CRUD operations on the Employee table in the data store using the client object as follows.
// Create a new `employee` record. EmployeeInsert employee = {id: 1, name: "John", age: 30, salary: 3000.0}; int[]|error employeeId = sClient->/employees.post([employee]); // Get the `employee` record with the ID 1. Employee|error employee = sClient->/employees/1; // Update the `employee` record with the ID 1. Employee|error updated = sClient->/employees/1.put({salary: 4000.0}); // Delete the employee record with the ID 1. Employee|error deleted = sClient->/employees/1.delete(); // Get records of all employees. stream<Employee, error?> employees = sClient->/employees;
Learn more about persist client APIs in the Client API section.